How to Read Whisker and Box Graph
Contents (Click to skip to that section):
- What is a Boxplot?
- How to Read a Box Plot
- How to Brand a Box Plot:
- Excel
- TI-83
- TI-89
- SPSS
- Minitab
What is a Boxplot?
Watch the video for an overview and how to make one by hand:
Tin't see the video? Click here.
The box and whiskers chart shows you how your data is spread out. V pieces of data (the "five number summary") are generally included in the chart:
- The minimum (the smallest number in the data set). The minimum is shown at the far left of the chart, at the end of the left "whisker."
- Offset quartile, Q1, is the far left of the box (or the far correct of the left whisker).
- The median is shown as a line in the center of the box.
- Third quartile, Q3, shown at the far right of the box (at the far left of the right whisker).
- The maximum (the largest number in the data prepare), shown at the far right of the box.
Back to Superlative
How to Read a Box Plot
A boxplot is a way to testify a five number summary in a chart. The principal role of the nautical chart (the "box") shows where the centre portion of the data is: the interquartile range. At the ends of the box, y'all" detect the beginning quartile (the 25% mark) and the third quartile (the 75% mark). The far left of the chart (at the terminate of the left "whisker") is the minimum (the smallest number in the gear up) and the far right is the maximum (the largest number in the set). Finally, the median is represented past a vertical bar in the heart of the box.
Box plots aren't used that much in real life. Still, they can be a useful tool for getting a quick summary of information.
How to Read a Box Plot: Steps
Step 1: Find the minimum.
The minimum is the far left hand side of the graph, at the tip of the left whisker. For this graph, the left whisker end is at approximately 0.75.
Step 2: Find Q1, the first quartile.
Q1 is represented by the far left hand side of the box. In this case, nearly ii.five.
Step 3: Detect the median.
The median is represented by the vertical bar. In this boxplot, it can exist found at nigh 6.5.
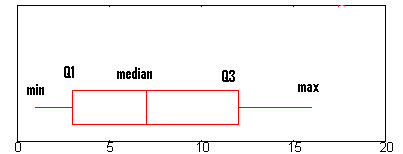
Step four: Find Q3, the third quartile.
Q3 is the far right hand edge of the box, at about 12 in this graph.
Step five: Find the maximum.
The maximum is the end of the "whiskers": in this graph, at approximately xvi.
Instance 2
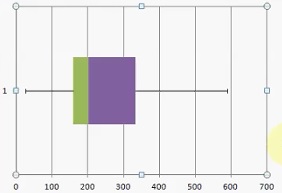
Y'all can hands read a boxplot to find the v number summary. For example, the above image shows a box and whiskers chart with the following information:
- Minimum: xx
- Q1: 160
- Median: 200
- Qthree: 330
- Maximum: 590
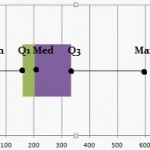
Exception: If your data gear up has outliers (values that are very loftier or very low and fall far exterior the other values of the information set), the box and whiskers chart may not show the minimum or maximum value. Instead, the ends of the whiskers represent one and a half times the interquartile range (1.v*IQR).
All done. That's how to read a box plot!
Similar the caption? Cheque out the Practically Cheating Statistics Handbook, which has hundreds more step-past-step solutions, merely like this ane!
Notation on Outliers:
Data sets can sometimes contain outliers that are suspected to be anomalies (mayhap because of data collection errors or only plain one-time flukes). If outliers are present, the whisker on the appropriate side is drawn to 1.5 * IQR rather than the data minimum or the information maximum. Small circles or unfilled dots are drawn on the chart to signal where suspected outliers lie. Filled circles are used for known outliers.
Check out our YouTube channel for hundreds of basic statistics videos.
Back to Top
How to Make a Box and Whiskers Chart
Excel
Watch this video on How to Brand a Box and Whiskers Chart in Excel.
Tin't come across the video? Click hither.
Excel does not accept a box and whiskers "Insert Graph" part, so you have to build one using stacked bar charts. This is a little more time-consuming than inserting a unproblematic graph, only it you will end up with a neat looking box and whiskers graph.
Note: This is an advanced Excel technique, so if yous are new to Excel you may want to watch the video, which has more data and visuals for each step to make a box and whiskers chart in Excel.
How to Make a Box and Whiskers Chart in Excel: Steps
Sample problem: Make a box and whiskers chart in Excel for the following data set: 25, 145, 145, 148, 178, 178, 198, 201, 222, 210, 565, 589, 485, 333, 358, 158, 257.
Step i: Type your information into one column in an Excel worksheet. For this case, blazon your data into cells A1:A11.
Step 2: Click an empty cell type "MIN, Q1, MED, Q3 and MAX" in a single cavalcade. In the adjacent column over, type formulas for MIN, Q1, MED and MAX. The formulas are:
- =MIN(A1:A17)
- =QUARTILE(A1:A17,1)
- =MED(A1:A17)
- =QUARTILE(A1:A17,three)
- =MAX(A1:A17)
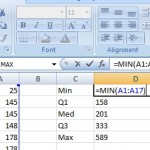
Pace 3: In the next column over, type your Min (in this case, 25) into the jail cell next to the Min you calculated.
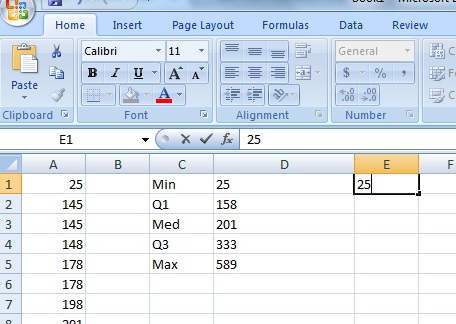
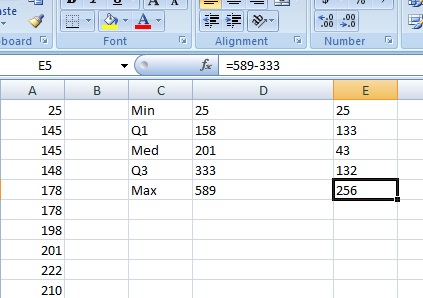
Pace 4: Decrease each value in the previous cavalcade from the next value. In other words, decrease the Min from Q1, the Q1 from the Med, the Med from Q3 and Q3 from the Max.
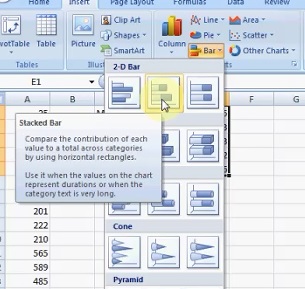
Step five: Highlight the column of differences you calculated in Step 4, then click "Insert," then click "Bar" and then click "Stacked Bar."
Steps half dozen – 10
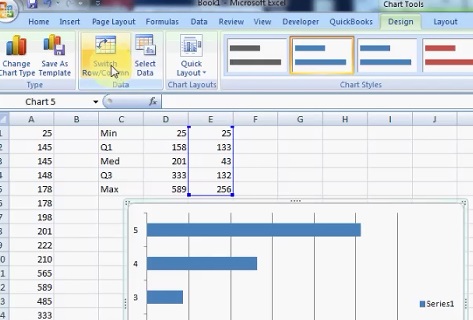
Step 6: Click the graph and and so click the "Switch Row/Column" button.
Step vii: Select the left-hand blue box, right-click and and so click "Format Data Series."
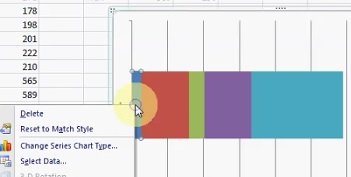
Stride 8: Click "Make full," then click the "No Fill" radio button and and then click "Close."
Step ix: Add together the whisker to the left-hand side using the post-obit method:
- Click the left-mitt red box.
- Select the "Layout" tab, then click "Fault Bars". Next, click "More Fault Bar Options."
- Click "Error Bars with Standard Fault."
- Select the "Layout" tab again, and then click "Mistake Bars" and then click "More Mistake Bar Options."
- Click "Mins" and then type the difference between Q1 and the Min into the "Fixed Value" box. For this sample problem, that value is 133.
- Click "Close."
- Remove the cherry color (fill) using the technique outlined in Steps seven and 8 above.
Stride 10: Add together the whisker to the right-manus side of the box and whiskers chart Excel using the following method:
- Click the purple box.
- Select the "Layout" tab, so click "Error Bars" → "More Error Bar Options."
- Click "Mistake Bars with Standard Error."
- Select the "Layout" tab once more, then click "Error Bars" → "More than Error Bar Options."
- Click "Plus" and and then blazon the divergence between Q3 and the Max into the "Fixed Value" box. For this sample problem, that value is 256.
- Click "Close."
- Remove the light-blue color (fill) using the technique outlined in Steps vii and 8 in a higher place.

That's it: Yous've created a box and whiskers nautical chart in Excel!
Step 11: (Optional) Delete the "Series" information from the right: Click the name and then press the "Delete" central.
Tip: If you don't see an error bar evidence up, that's probable because y'all demand to change the line color to "Black" from the More Error Bar Options window.
Cheque out our YouTube channel for more Excel help and tips!
Back to Superlative
TI 83 box plot: Overview
Let's say you accept a list of IQ scores for a gifted classroom in a particular unproblematic school. The IQ scores are: 118, 123, 124, 125, 127, 128, 129, 130, 130, 133, 136, 138, 141, 142, 149, 150, 154. That list doesn't tell you much nearly anything. However, with a TI 83 box plot, the data tin come up to life.
Steps
You may detect this article helpful if you lot've never entered a list into the calculator before: Inbound lists on a TI 83.
Step i: Press STAT, and so ENTER, to edit list L1.
Step ii: Enter the data from the problem into the list (one value on each line, don't enter the commas):
118, 123, 124, 125, 127, 128, 129, 130, 130, 133, 136, 138, 141, 142, 149, 150, 154.
Step 3: Printing 2nd Y=, to access the Stat Plot menu.
Footstep four: Press ENTER ENTER to plow on Plot1.
Pace 5: Pointer downwardly to Blazon, which has half-dozen icons to the right of it. Highlight the bottom middle icon, which looks like a syringe with ii plungers, and press ENTER to select it.
Step 6: Make sure the XList entry reads "L1". If it doesn't, pointer down to information technology, Press Articulate 2nd 1.
Pace 7: Press Graph. You should run across your Box plot.
Tip: If when yous printing Graph, you see the message "Err: Stat", or you lot only don't see a box plot like y'all expect to, then press Window, and try different settings. Specially attempt irresolute the Xscl (X Scale) item to a larger value.
TI-89
Instance problem: Create a box and whiskers nautical chart with the following data: 100, 340, 400, 350, and 400.
Stride 1: Create a new binder called "Box." From the Dwelling screen, printing F4 and scroll downwards to NewFold (option B). Press ENTER.
Footstep two: Press 2d Alpha ( – ten to spell B O X and press ENTER.
Pace three: Press APPS, so scroll down to Stats/List Editor. Press ENTER twice.
Step iv: Printing the down pointer key to get to the first line of the list. Enter your data into list1. Follow each entry with a comma: 100, 340, 400, 350, 400.
Stride 5: Press F2 then 1 to enter Plot Setup.
Step 6: Printing F1, right arrow, and 5 to select mod box plot.
Footstep 7: Pointer down to Marker and select box.
Pace eight: Arrow downwards and enter B O Ten (using the alphanumeric keypad) in the x. Press ENTER.
That's information technology!
Back to Top
SPSS
SPSS allows yous to create two types of boxplots: simple and clustered. Which type of boxplot you choose depends upon how many variables you want to plot. Cull the simple chart choice when you desire to create a plot of one variable, and cull the amassed boxplot option if you want to create a comparison of variable types. SPSS boxplots can be created in the Chart Architect or in the Legacy Dialogs carte.
Box plot in SPSS: Steps
Watch the video to run into how to make a boxplot in SPSS using the Chart Builder, or read the steps below for a slightly dissimilar way to make a boxplot in SPSS, by using the legacy dialog.
Tin can't see the video? Click here.
Stride i: Open an existing worksheet with your data or type your data into a new worksheet.
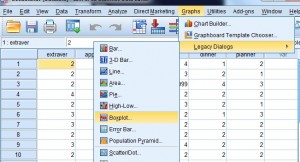
Step 2: Click "Graphs," then click "Legacy Dialogs" and and then click "Boxplot."
Step 3: Click the blazon of chart you desire to display, either Unproblematic or Amassed, then click a radio button for either summaries of groups or separate variables.
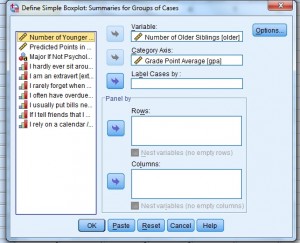
Step four: Click "Ascertain" to open the "Ascertain Simple Boxplot" dialog box.
Pace 5: Click a variable in the left window that you desire to encounter medians or IQRs for. This is the analytical variable, the one that will be displayed on the y-axis. Click the top pointer to move the variable to the "Variable" window.
Stride 6: Click a second variable in the left window that you desire to brandish on the x-axis (the chiselled variable), and so click the second arrow down, to the left of Category Axis.
Stride 7: Click "OK" to display the boxplot.
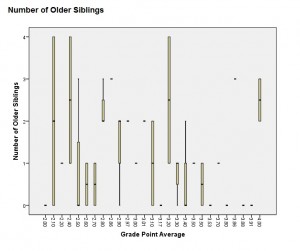
Minitab Box Plot
Thanks to Minitab's easy-to-utilise graph cosmos software, y'all tin make a box plot in Minitab in a couple of clicks. Watch this video on how to make a box plot in Minitab:
Can't see the video? Click here.
Step 1: Type your data into columns in a Minitab worksheet. Typically, you'll desire to blazon in 2 columns of data, one categorical and one quantitative (numerical).
Step 2: Click "Graph" on the toolbar and then click "Boxplot."
Stride three: Choose a blazon of boxplot. If your information is in the course of column of quantitative data and ane column of categorical variables (the most common scenario) then cull "One y" "With groups".
Footstep iv: Click a variable name for your quantitative/numerical data and then click "Select" to move the detail to the Graph Variables box.
Step five: Click a variable proper noun for your categorical information and and then click "Select" to move that item to the Categorical Variables box.
Footstep 4: Click "OK" to create a boxplot.
That's it!
Tips: Mouse over one of the boxes to brandish a window showing the median, Q1, Q3 and the IQR. You tin can also click on a number to bring up the Edit Scale box to specify labels, scales and other attributes for the boxplot.
Back to Superlative
References
Gonick, L. (1993). The Cartoon Guide to Statistics. HarperPerennial.
Kotz, South.; et al., eds. (2006), Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences, Wiley.
Wheelan, C. (2014). Naked Statistics. Due west. Due west. Norton & Visitor
Salkind, Northward. (2016). Statistics for People Who (Think They) Hate Statistics: Using Microsoft Excel 4th Edition.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Need help with a homework or test question? With Chegg Study, you lot can go footstep-past-step solutions to your questions from an proficient in the field. Your first 30 minutes with a Chegg tutor is free!
Comments? Need to post a correction? Please post a comment on our Facebook page .
Source: https://www.statisticshowto.com/probability-and-statistics/descriptive-statistics/box-plot/#:~:text=The%20far%20left%20of%20the%20chart%20(at%20the%20end%20of,that%20much%20in%20real%20life.
0 Response to "How to Read Whisker and Box Graph"
Post a Comment